Would you like to make this site your homepage? It's fast and easy...
Yes, Please make this my home page!
HOME~~~PREV~~~NEXT
~~~ DESCRIPTION OF KOCH THERAPY ~~~
1. detoxification:
ptomaines, certain foods,
xenobiotics, (metals)
2. oxygenation
3. catalyst administration
~~~ DISEASES TREATABLE ~~~
allergies 70-80%
infections 50-80%
neoplasms 50+%
misc. 50+%
~~~ CATALYSTS USED BY KOCH ~~~
PARAQUINONES: parabenzoquinone, diphenoquinone
ORTHOQUINONES: triquinoyl, rhodozonic acid
GLYOXALS: glyoxal, methylglyoxal, diacetyl,
"glyoxylide"
~~~ SPECIAL CHARACTERISTICS ~~~
= conjugated dicarbonyl compounds
= extremely dilute ( 6X to 12X )
= stable in glass ampuoles
= capable of penetrating tissues
= exist in three valences
= redox active at an intermediate potential
= capable of redox cycling in vivo
NOTE: This is the only reaction that is repeatable
indefinitely and can therefore account for
activity at such infinitesimal doses.
~~~ CLASSES OF REDOX CYCLING COMPOUNDS ~~~
1) para-benzoquinones
2) para-naphthoquinones
3) para-anthroquinones
4) orthoquinones/tannins
5) alphaketoaldehydes &
alphaketoketones
6) heterocyclic compounds
7) multivalent elements
~~~ THREE VALENCES OF PARAQUINONES ~~~
HC==CH
/ \
PARAQUINONE: O==C C==O
Q \ /
HC==CH
HC==CH
/ \
SEMIQUINONE: *O--C C--OH
*QH \\ //
HC--CH
HC==CH
/ \
PARAHYDROQUINONE: HO--C C--OH
QH2 \\ //
HC--CH
~~~ THREE VALENCES OF GLYOXALS ~~~
R R R R
| [H] | | [H] |
O==C ---> HO--C* HO--C ---> HO--C
| [O] | <---> || [O] ||
C==O <--- C==O C--O* <--- C--OH
| | | |
R R R R
OGO *OGOH HOGOH
EXAMPLES: glyoxal, methylglyoxal, diacetyl, "glyoxylide"
orthoquinones, tannins, triquinoyl, rhodizonic acid
dehydroascorbic acid, pyrroloquinoline quinone
~~~ FIVE MECHANISMS ~~~
Five mechanisms exist whereby redox cycling can profoundly
deplete electrons/hydrogen from various physiolic carriers:
1) quinone type redox cycling
2) superoxide production
3) hydrogen peroxide production
4) autoregeneration of H2O2
5) immunoactivation producing ROS
at the sight of pathology
~~~ REDUCTANT DEPLETING MECHANISMS FOR QUINONES ~~~
1. Direct dehydrogenation of various substrates
XH + Q ---> X* + HQ*
XH2 + Q ---> HX* + HQ*
XH2 + Q ---> X + QH2
followed by oxidative reactivation
HQ* + [O] ---> Q + [HO*]
QH2 + [O] ---> Q + H2[O]
2. Superoxide/hydroperoxyl radical production
*QH + O2 ---> Q + -OO* + H+
*XH + O2 ---> X + -OO* + H+
HOO* + AOH ---> HOOH + AO*
3. Hydrogen peroxide production
HOO* + AOH ---> AO* + HOOH
2(-OO*) + 2H+ ---> O2 + HOOH
2GSH + HOOH ---> GSSG + 2H2O
4. Autoregeneration of hydrogen peroxide
HOOH + P ---> P**
2HXH + P** ---> 2HX* + P + 2HOH
2HX* + 2OO ---> 2X + 2-OO* + 2H+
2-OO* + 2H+ ---> OO + HOOH
=== 2HXH + OO ---> 2X + 2HOH ===
~~~ REDUCTANTS AS SUBSTRATES ~~~
These can lose electrons to quinones:
Amines:
hydropyridines, leukoflavins
Enediols:
ascorbates, bioflavonoids
Phenols:
tocopherols, ubiquinols
Thiols:
glutathione, proteins
Aldehydes
Multivalent Metals:
Fe++ or Cu+
~~~ OXIDANTS AS RECYCLERS ~~~
These can reoxidize semiquinones and dihydroquinones.
Oxygen Compounds:
*OO* , O=O , HOOH
Oxyradicals:
HO* , HOO* , RO* , ROO*
Hypochlorous Acid: HClO
Multivalent Metals:
Fe+++ (peroxidases,cytochromes)
Cu++ (ceruloplasmin)
~~~ "ENZYMES AND METABOLIC INHIBITORS" ~~~
by J. Leyden Webb, School of Medicine,
University of Southern California, Los Angeles,
Academic Press, 1966, Volume 3, Chapter 5, pp 421-594
TOPICS DISCUSSED:
structural formulae of quinones, effects of attached groups,
oxidation-reduction reactions, addition reactions,
tables of enzymes inhibited, mechanisms of inhibition,
effects on electron transport, oxidative phosphorylation,
effects on glycolysis, respiration, metabolic systems,
effects on tissue functions, whole animals,
antimitotic actions, effects on neoplastic cells,
antibacterial activity, effects on fungi,
effects on algae, protozoa, invertebrates, viruses,
effects of quinone like imines
~~~ QUINONE TYPES AND EXAMPLES ~~~
BENZOQUINONES: parabenzoquinone uva ursi
C==C methoxybenzoquinone wheat
/ \ plastoquinone algae
O==C C==O ubiquinone heart
\ /
C==C
NAPTHOQUINONES: menadione vit K
C==C lapachol pau-de-arco
/ \ plumbagin lead wort & VFT
O==C C==O juglone black walnut
\ / lawsone henna
RING
ANTHROQUINONES: emodin senna & cascara
RING aloe-emodin aloe vera rind
/ \ rhein rhubarb root
O==C C==O hypericin St.John's wort
\ /
RING
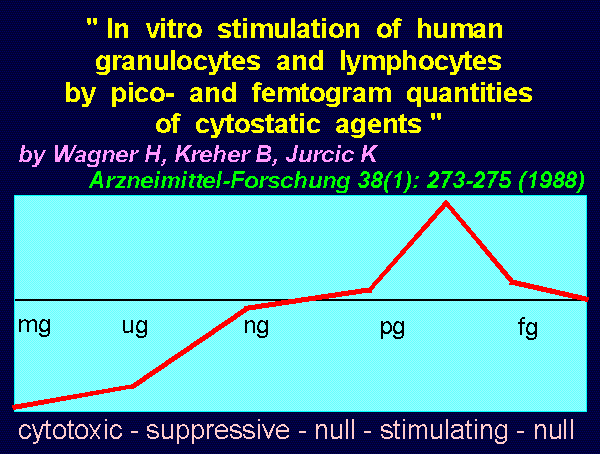
"In vitro stimulation of human granulocytes and lymphocytes
by pico- and femtogram quantities of cytostatic agents"
by Wagner H, Kreher B, Jurcic K
Arzneimittel-Forschung 38(1): 273-275 (1988)
DOSAGE RANGES: RESULTS:
mg to ug cytotoxic
ug to ng suppressive
ng to pg null
pg to fg stimulatory
fg to ag null
These results correspond to concentrations calculable
in vivo after injection of a Koch catalyst.
~~~ HINDERING AGENTS ~~~
1) amines such as methylguanidine
inhibit diamine oxidase
may inhibit carbonyl compounds in other BETS
2) sulfides especially hydrogen sulfide
like cyanide strongly inhibit cytochrome A
3) toxic metals such as selenite overdose
bind to thiols so as to block electron transfers
4) citrus fruit
contains citric acid which inhibits ceruloplasmin
may supply turpenes from the rind
5) xenobiotic detox stimulants:
(e.g. alcohols, turpenes, aromatics, organic chlorides)
enhance phase II conjugases & accelerate catalyst removal
eliminate glutathione by induction of S-transferases
induce synthesis of quinone reductases & CP450 reductases
6) grapes
contains resveratrol which induces quinone reductase
~~~ HOW TO OVERCOME XENOBIOTIC INTERFERENCE ~~~
Select patients which are:
not already exposed excessively
not in need of many detox stimulating
drugs, foods, or herbs
not in a hyperactive detox condition
For those deemed in need of xenobiotics:
minimize exposure or utilization
treat nutritionally to ensure
sufficiency of GSH
repeat catalyst administration more often
switch to stronger oxidant therapies
(e.g. O3, ClO2, H2O2, UVHIT)
~~~ ENHANCING AGENTS ~~~
The following were found to supportive of recovery
per clinical experience of Dr. Koch:
* nutrition * PUFA's * oxygenation
* colon detoxification * copper * acute infection
* hydrogen peroxide * hemoirradiation * magnetic fields
~~~ WHAT ABOUT COFFEE ENEMAS ? ~~~
Several alternative health programs involve
the regular administration of coffee enemas.
This is thought by many to detoxify the liver
as caffeine stimulates bile flow.
However, the roasting of coffee beans is known to produce:
glyoxal, methylglyoxal, diacetyl,
and other dicarbonyl compounds.
Brewing is known to produce orthoquinones and
hydrogen peroxide, as caffeic acid and other
polyphenols auto-oxidize.
polyphenol + O2 ---> orthoquinone + H2O2
Thus brewed coffee is a mixture of glyoxals, orthoquinones,
and hydrogen peroxide, all of which are pro-oxidant.
Much of the immune system is present in the lymphoid
tissues of the gut, which would be in close proximity
to the coffee.
This suggests that the real value of coffee enemas may be
oxidative stimulation of the immune system of the gut.
This would be similar in principle to rectal insufflation
of ozone, a known effective method.
HOME~~~PREV~~~NEXT
